Project management success in modern high-paced business operations depends heavily on the Project Management Office (PMO).
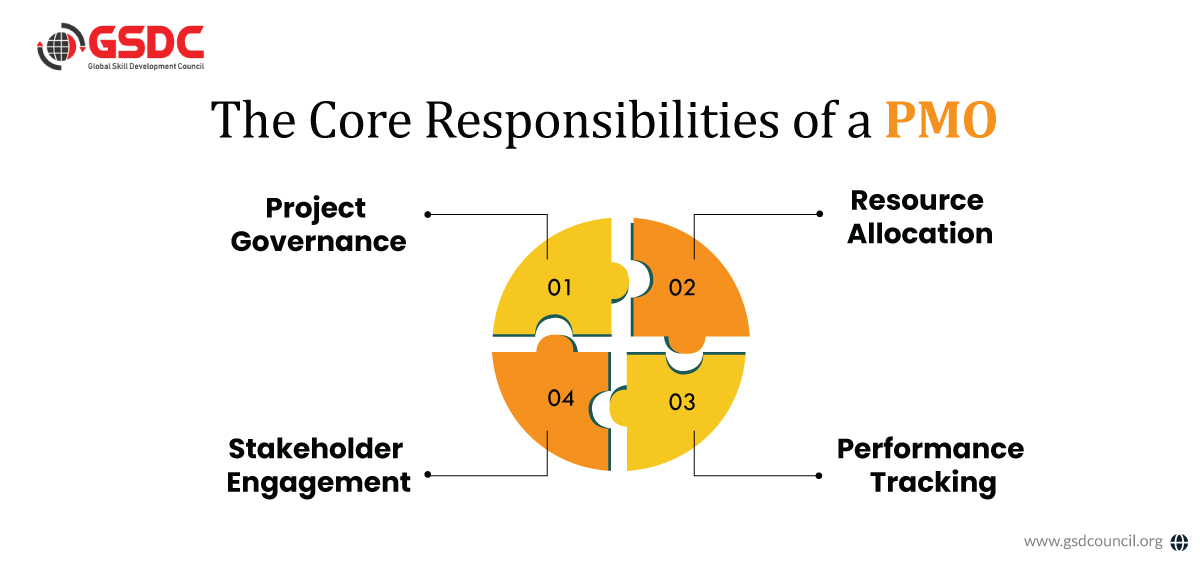
Within an organization, the project management officer exists as the vital institution that oversees project management structure through governance functions alongside resource management and performance monitoring.
The well-organized PMO helps businesses operate more efficiently by processing essential functions which leads to improved stakeholder relationships and overall business success.
In this article, we will explore the project management officer roles and responsibilities and their impact on project execution.
The Project Management Office (PMO) serves as a centralized entity within an organization that ensures projects are executed efficiently and align with business objectives.
The responsibilities of a PMO extend beyond simple project oversight; they encompass a broad range of activities that help streamline project execution, governance, and continuous improvement.
One of the core responsibilities of a PMO is to oversee the entire project lifecycle, from initiation to closure. This includes:
Strategic business goal alignment with project lifecycle control provided by PMO work reduces the occurrence of project failures.
Post-project evaluations form an essential part of the PMO's responsibilities for process optimization purposes while safeguarding against the recurrence of similar problems.
A PMO establishes governance frameworks and standardizes project management methodologies to maintain uniformity across different projects. These frameworks help in the following:
PMOs implement governance structures that establish project execution frameworks resulting in better success rates during project completion.
PMOs deliver administrative assistance along with guidelines about regulations and strategies that limit operational risk exposure.

A PMO serves multiple functions that enhance project performance and efficiency.
Beyond governance and lifecycle management, the PMO plays an integral role in fostering collaboration, optimizing resources, and ensuring project success.
Effective resource management is a fundamental role of the PMO. This includes:
By efficiently managing resources, a PMO prevents burnout, improves team productivity, and ensures projects are completed within budget and timelines.
The ability to align human capital and financial assets effectively contributes to overall organizational success.
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) allows a PMO to assess project health and efficiency. Common KPIs include:
Project managers who conduct routine performance checks will discover potential risks at an early stage and implement corrective measures thus reducing overall project failures.
Real-time dashboards alongside reporting tools within PMOs offer decision-relevant insights to management for better choices and permanent project execution development.
Engaging with stakeholders ensures alignment between project objectives and business goals.
A PMO’s stakeholder engagement strategy includes:
The PMO maintains positive stakeholder relations to increase project collaboration which secures organizational backing for initiatives.
The success rates of projects increase along with their alignment to strategic goals when stakeholders are effectively managed.
PMOs can be structured in different ways based on an organization’s needs. The three primary types include:
By implementing a PMO structure suited to the organization’s needs, businesses can maximize project efficiency and enhance overall governance.

The presence of a Project Management Office (PMO) is critical for businesses that want to improve project success rates and ensure optimal use of resources.
Below are key reasons why PMOs are essential in organizations:
Research highlights that organizations with a structured PMO experience higher success rates.
For example:
A well-defined PMO can improve resource allocation efficiency by 30%, leading to better project portfolio management.
PMOs ensure that resources are distributed based on priority and project requirements, preventing delays and conflicts over personnel.
PMOs act as a bridge between strategy and execution, ensuring that projects contribute to the company’s long-term objectives.
By enforcing standardized governance and frameworks, PMOs:
One of the primary functions of a PMO is identifying potential risks early in the project lifecycle.
Through continuous monitoring and risk assessment methodologies, PMOs:
PMOs play a vital role in fostering continuous improvement within project management practices by:
By emphasizing these areas, PMOs ensure that organizations improve their operational efficiencies and project management capabilities over time.
A professional PMO certification creates a significant career impact by strengthening their project management expertise together with PMO best practices.
Organizations seek the GSDC Certified PMO Professional qualification to confirm and coordinate offerings that enable professionals to launch and lead PMO operations effectively.
If you're looking to advance your career and enhance your understanding of project management officer roles and responsibilities, this certification can provide a structured pathway to success.
Despite their importance, PMOs encounter several challenges that can hinder their ability to function effectively. Some of the most common challenges include:
Many project teams and departments resist adopting new methodologies and governance models imposed by the PMO. This resistance can stem from:
Overcoming resistance requires effective change management strategies, regular communication, and leadership buy-in to demonstrate the value of the PMO.
Without support from senior leadership, a PMO may struggle to enforce governance policies and secure the necessary resources. Common challenges include:
Ensuring alignment between the PMO and business objectives and demonstrating ROI through project performance metrics can help gain executive sponsorship.
One of the biggest challenges PMOs face is proving their value to the organization. Measuring ROI can be difficult because:
To address this, PMOs should implement KPIs that clearly demonstrate improvements in project success rates, cost savings, and resource utilization.
A PMO needs skilled professionals, technological tools, and a structured approach to function effectively. However, many PMOs face:
Organizations should consider incremental PMO development and prioritize investment in technology and personnel to enhance PMO effectiveness.
As project management continues to evolve, PMOs must adapt to new trends and innovations to maintain relevance and efficiency. Key future developments include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing an increasing role in project management. AI-driven tools enable:
With organizations shifting toward Agile methodologies, PMOs must become more adaptable by:
As businesses undergo rapid transformations, PMOs must:
The future of PMOs depends on big data and analytics which enables them to track projects better while foreseeing risks and optimizing resource management initiatives.
PMOs can establish their role as strategic success and innovation facilitators through the adoption of these trends.
The Project Management Office (PMO) ensures project success by applying its governance functions and resource management and performance monitoring as well as stakeholder engagement capabilities.
Through best practices, the PMO creates more efficient operations and lowers project failure rates while connecting projects with organizational goals.
Project success rates together with better resource allocation and strategic decision-making result from organizations that develop thorough PMO structures.
Modern business operations will benefit from the increasing significance of PMOs because they will add new methodologies and technologies to their existing framework.
If you like this read then make sure to check out our previous blogs: Cracking Onboarding Challenges: Fresher Success Unveiled
Not sure which certification to pursue? Our advisors will help you decide!